In the digital age, data security remains one of the most critical aspects of technology and communication. As we progress into 2024, the evolution of cryptographic keys—an essential component of modern data security—is undergoing significant transformations. Emerging technologies are reshaping how cryptographic keys are created, managed, and protected, thereby redefining the landscape of data security. This article delves into these advancements and their implications for safeguarding sensitive information.
1. Introduction to Cryptographic Keys
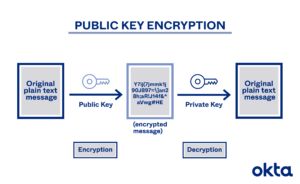
Cryptographic keys are fundamental to securing digital communication and protecting data integrity. They are used in various encryption algorithms to encode and decode information, ensuring that only authorized users can access it. Traditionally, cryptographic keys come in two types: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric keys use a single key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric keys employ a pair of keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
2. Advancements in Key Management
In 2024, key management systems (KMS) are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Modern KMS solutions incorporate advanced features such as automated key rotation, enhanced access controls, and real-time monitoring. Automated key rotation ensures that cryptographic keys are updated regularly without manual intervention, reducing the risk of exposure due to stale keys. Enhanced access controls, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC), provide additional layers of security by restricting key usage to authorized personnel only.
Moreover, real-time monitoring capabilities enable organizations to detect and respond to potential security incidents promptly. These systems generate alerts for suspicious activities and unauthorized access attempts, allowing for swift remediation and minimizing the impact of potential breaches.
3. Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
As quantum computing advances, traditional cryptographic algorithms face potential threats. Quantum computers have the potential to break widely used encryption methods, such as RSA and ECC, by leveraging their superior processing power. To address this concern, researchers are developing quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms that can withstand attacks from quantum computers.
In 2024, the field of post-quantum cryptography is gaining momentum. Algorithms such as lattice-based cryptography, hash-based cryptography, and code-based cryptography are being explored for their ability to resist quantum attacks. These quantum-resistant algorithms are being integrated into new cryptographic systems, providing a future-proof solution for data security.
4. Blockchain and Cryptographic Keys
Blockchain technology continues to revolutionize data security and cryptographic key management. By design, blockchain systems use cryptographic keys to ensure the integrity and immutability of data stored on the blockchain. Public and private keys are essential for verifying transactions and securing digital assets.
In 2024, blockchain-based solutions are being utilized to enhance key management practices. Decentralized key management systems leverage the distributed nature of blockchain to eliminate single points of failure and improve security. Additionally, smart contracts on blockchain platforms automate key management tasks, such as key issuance and revocation, further enhancing the efficiency and security of cryptographic systems.
5. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs)
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) play a crucial role in protecting cryptographic keys from physical and logical attacks. HSMs are specialized hardware devices designed to generate, store, and manage cryptographic keys securely. They are commonly used in financial institutions, government agencies, and other sectors requiring high levels of data protection.
In 2024, HSMs are evolving to meet the growing demands for security and performance. Newer models incorporate advanced features such as tamper-evident technology, secure key storage, and enhanced cryptographic capabilities. Additionally, cloud-based HSM services are gaining popularity, offering scalable and cost-effective solutions for managing cryptographic keys in the cloud.
6. Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
Several emerging technologies are influencing the evolution of cryptographic keys in 2024:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to enhance key management and cryptographic processes. Machine learning algorithms can analyze large volumes of data to detect anomalies and predict potential security threats. AI-driven key management systems can automate tasks such as key generation, rotation, and access control, improving overall efficiency and security.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of IoT devices introduces new challenges for cryptographic key management. With billions of connected devices generating and transmitting data, securing these devices requires robust cryptographic solutions. IoT devices are increasingly incorporating hardware-based security features and secure key storage to protect sensitive information.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance. However, it also introduces new security challenges. Cryptographic keys used in edge computing environments need to be managed and protected across distributed locations. Edge devices are being equipped with enhanced security features to safeguard cryptographic keys and ensure data integrity.
7. Future Trends and Considerations
Looking ahead, several trends and considerations will shape the future of cryptographic keys:
- Increased Focus on Privacy: With growing concerns about data privacy, cryptographic solutions are placing greater emphasis on protecting personal information. Techniques such as homomorphic encryption, which allows computations on encrypted data without decrypting it, are gaining traction as privacy-preserving solutions.
- Regulatory Compliance: As regulations around data protection become more stringent, organizations must ensure that their cryptographic practices comply with relevant standards and laws. Compliance frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), are driving the adoption of robust cryptographic measures.
- Integration with Zero Trust Architecture: The Zero Trust security model, which assumes that no entity—inside or outside the network—is trusted by default, is becoming more prevalent. Cryptographic keys play a critical role in Zero Trust architectures by providing secure authentication and access control mechanisms.
8. Conclusion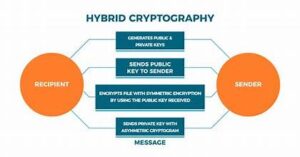
The evolution of cryptographic keys in 2024 is marked by significant advancements driven by emerging technologies. From enhanced key management systems and quantum-resistant cryptography to the integration of blockchain and AI, these developments are reshaping the landscape of data security. As organizations navigate the complexities of securing their data, staying informed about these advancements and adopting best practices will be crucial for maintaining robust protection against evolving threats.