In an era where data breaches and cyberattacks are increasingly prevalent, the evolution of cryptographic keys has never been more critical. As we advance into 2024, emerging technologies are transforming how cryptographic keys are generated, managed, and protected. This article delves into the latest developments in cryptographic keys, exploring how these innovations are enhancing data security and what they mean for the future of cybersecurity.
Understanding Cryptographic Keys
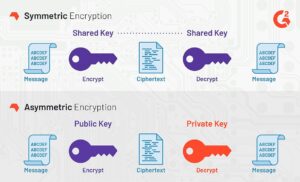
Cryptographic keys are the cornerstone of modern data security. They are used to encrypt and decrypt information, ensuring that only authorized parties can access sensitive data. There are two main types of cryptographic keys: symmetric and asymmetric.
- Symmetric Keys: These use a single key for both encryption and decryption. The challenge with symmetric keys lies in securely sharing the key between parties.
- Asymmetric Keys: Also known as public-key cryptography, this method uses a pair of keys—one public and one private. The public key encrypts the data, while the private key decrypts it. This method enhances security by eliminating the need for key exchange.
The State of Cryptographic Keys in 2024
As we move through 2024, several key trends and technologies are reshaping the landscape of cryptographic keys:
1. Post-Quantum Cryptography
Quantum computers pose a significant threat to current cryptographic methods. These machines have the potential to break encryption that relies on traditional mathematical problems. To counter this threat, researchers are developing post-quantum cryptographic algorithms. These algorithms are designed to be resistant to quantum attacks, ensuring that data remains secure even in a quantum computing era.
Key Developments:
- NIST’s Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization: The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is leading the charge in standardizing post-quantum cryptographic algorithms. Their efforts aim to provide robust, quantum-resistant encryption solutions that can be widely adopted.
2. Blockchain and Decentralized Key Management
Blockchain technology is making waves in the world of cryptography. Its decentralized nature offers a new approach to key management, enhancing security and transparency.
Key Developments:
- Decentralized Identity (DID) Systems: These systems use blockchain to manage digital identities and associated cryptographic keys. They enable users to have greater control over their personal data and reduce the risk of centralized data breaches.
3. Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs)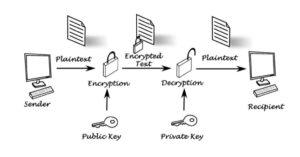
Zero-Knowledge Proofs are a groundbreaking technology that allows one party to prove to another that a statement is true without revealing any additional information. This technology is increasingly being integrated into cryptographic protocols to enhance privacy and security.
Key Developments:
- zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs: These are types of ZKPs that offer efficient, scalable solutions for privacy-preserving transactions. They are being used in various applications, including cryptocurrency transactions and secure voting systems.
4. Biometric and Multi-Factor Authentication
As security threats evolve, so too do authentication methods. Biometric authentication, combined with multi-factor authentication (MFA), is becoming a standard practice to enhance the security of cryptographic keys.
Key Developments:
- Advanced Biometric Systems: Modern biometric systems, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, are becoming more sophisticated. They are used to secure access to devices and sensitive information.
- Enhanced MFA Solutions: Multi-factor authentication now includes a combination of something you know (password), something you have (smartphone), and something you are (biometric data). This layered approach significantly increases security.
5. Quantum-Resistant Hardware Security Modules (HSMs)
Hardware Security Modules are physical devices used to manage and protect cryptographic keys. As quantum computing advances, quantum-resistant HSMs are being developed to safeguard these keys against quantum attacks.
Key Developments:
- Integration of Post-Quantum Algorithms: New HSMs are integrating post-quantum cryptographic algorithms to future-proof key management systems against quantum threats.
Implications for Data Security
The evolution of cryptographic keys has significant implications for data security:
- Enhanced Protection Against Emerging Threats: With the advent of post-quantum cryptography and advanced encryption techniques, data security is becoming more robust, offering protection against future threats.
- Improved Privacy: Technologies like Zero-Knowledge Proofs are enhancing privacy by allowing transactions and communications to occur without revealing sensitive information.
- Greater Control and Transparency: Blockchain-based key management systems provide users with greater control over their data and reduce the risk of centralized data breaches.
- Strengthened Authentication: The integration of biometric and multi-factor authentication methods ensures that access to cryptographic keys is secure and that unauthorized access is minimized.
Conclusion
The evolution of cryptographic keys in 2024 reflects the rapid advancements in technology and the growing need for robust data security solutions. Post-quantum cryptography, blockchain technology, Zero-Knowledge Proofs, biometric authentication, and quantum-resistant hardware are all playing pivotal roles in shaping the future of data security. As these technologies continue to develop, they will undoubtedly enhance our ability to protect sensitive information and mitigate emerging threats.



