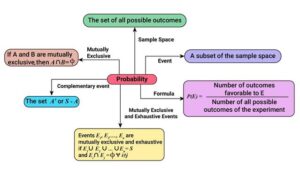
Probability theory is a fascinating branch of mathematics that not only serves as the foundation for statistics but also plays a crucial role in understanding and managing risk. From insurance and finance to everyday decisions, the principles of probability can illuminate the uncertainties of life. In this article, we will explore ten surprising facts about probability theory that might just change your perspective on risk.
1. Probability is Not Just About Gambling
While many associate probability theory with gambling, its applications extend far beyond the casino. Probability is used in diverse fields such as finance, healthcare, insurance, and even artificial intelligence. For example, in healthcare, probability can help assess the effectiveness of a new drug by determining the likelihood of patient recovery. Understanding these applications can shift your perspective on risk and its management.
2. The Law of Large Numbers
The Law of Large Numbers is a cornerstone of probability theory, stating that as a sample size increases, the sample mean will get closer to the expected value. This principle helps explain why large datasets often yield more accurate predictions than smaller ones. For instance, consider a company forecasting sales. By analyzing historical data over a larger time frame, the company can make more reliable predictions, thus better managing financial risk.
3. The Gambler’s Fallacy
The Gambler’s Fallacy is a common misconception where individuals believe that past random events can influence future outcomes in independent events. For example, if a coin lands on heads five times in a row, someone might think tails is “due.” Understanding this fallacy can help individuals make more rational decisions and avoid unnecessary risk based on flawed reasoning.
4. Expected Value and Decision-Making
Expected value is a vital concept in probability theory that represents the average outcome of a decision when accounting for all possible scenarios. This principle can guide individuals and businesses in making informed decisions. For instance, when considering an investment, calculating the expected value can reveal whether the potential returns outweigh the risks. Recognizing the power of expected value can fundamentally change how you approach risk.
5. The Importance of Base Rates
Base rates refer to the general prevalence of an event within a given population. Many people tend to ignore base rates when assessing risk, focusing instead on specific case details. For instance, when evaluating the likelihood of developing a certain disease, understanding the base rate can provide a clearer perspective on personal risk. Incorporating base rates into decision-making can lead to more accurate risk assessments.
6. Risk Perception vs. Actual Risk
Our perception of risk often differs significantly from actual risk. Psychological factors, such as fear and familiarity, can distort our understanding of risk. For instance, people may overestimate the risk of rare but dramatic events (like plane crashes) while underestimating more common risks (like car accidents). Understanding this discrepancy can help individuals make more rational choices and manage their risks effectively.
7. The Monty Hall Problem
The Monty Hall Problem is a famous probability puzzle that demonstrates how counterintuitive probability can be. In the game, a contestant chooses one of three doors, behind one of which is a car (the prize) and behind the others are goats (not desirable). After the contestant picks a door, the host, who knows what’s behind the doors, opens one of the remaining doors to reveal a goat. The contestant is then given the option to stick with their original choice or switch to the other unopened door. Surprisingly, switching gives a 2/3 chance of winning the car, while sticking with the original choice only gives a 1/3 chance. This problem illustrates how our intuition about probability can often lead us astray.
8. Conditional Probability and Its Impact
Conditional probability measures the likelihood of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred. This concept is critical in fields such as finance, where it helps assess risk based on prior events. For instance, an investor might evaluate the risk of a stock drop based on recent market trends. Understanding conditional probability can refine risk assessments and improve decision-making.
9. The Power of Randomness
Randomness is often misunderstood; people tend to search for patterns even in purely random data. This tendency can lead to overconfidence in predicting outcomes. For example, in investing, many believe they can predict market trends based on past performance. However, markets are influenced by numerous unpredictable factors, making randomness a significant component of risk. Embracing the inherent randomness in many scenarios can lead to more prudent risk management strategies.
10. The Role of Simulation in Risk Management
Simulation is a powerful tool in probability theory that allows individuals and organizations to model complex systems and assess risk. Techniques like Monte Carlo simulations can help estimate the likelihood of various outcomes based on different variables. This approach is widely used in finance, insurance, and project management to evaluate risks and make informed decisions. Understanding how to leverage simulations can transform your perspective on risk and enhance decision-making processes.
Conclusion
Probability theory offers a wealth of insights that can profoundly alter our understanding of risk. From recognizing the importance of large sample sizes to understanding the nuances of expected value and base rates, these surprising facts illustrate the complexities of probability and its applications in everyday life. By embracing these principles, individuals can make more informed decisions, mitigate risks effectively, and ultimately gain a clearer perspective on the uncertainties that shape our world.