In today’s data-driven world, businesses generate an enormous amount of data daily. The ability to analyze and interpret this data effectively can provide significant insights, driving strategic decisions and business growth. Descriptive statistics is a powerful tool that helps in understanding and summarizing data. This article explores how descriptive statistics can transform your data analysis, providing actionable insights and driving business success.
Understanding Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics involves summarizing and organizing data to make it easily understandable. Unlike inferential statistics, which make predictions or inferences about a population based on a sample, descriptive statistics aim to describe the main features of a data set succinctly. The key components of descriptive statistics include measures of central tendency, measures of variability, and graphical representations.
Measures of Central Tendency
- Mean: The mean, or average, is the sum of all data points divided by the number of data points. It provides a general idea of the overall level of the data.
- Median: The median is the middle value in a data set when arranged in ascending or descending order. It is less affected by outliers and skewed data compared to the mean.
- Mode: The mode is the most frequently occurring value in a data set. It is useful in understanding the most common data point.
Measures of Variability
- Range: The range is the difference between the highest and lowest values in a data set. It provides a basic measure of variability.
- Variance: Variance measures the average squared deviation from the mean. It indicates how much the data points spread out from the mean.
- Standard Deviation: The standard deviation is the square root of the variance. It provides a measure of the average distance from the mean and is useful for understanding data dispersion.
Graphical Representations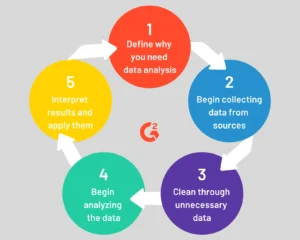
- Histograms: Histograms display the frequency distribution of a data set. They are useful for understanding the underlying distribution and identifying patterns.
- Box Plots: Box plots summarize data distribution, highlighting the median, quartiles, and potential outliers. They provide a visual representation of data spread and central tendency.
- Scatter Plots: Scatter plots display the relationship between two variables. They are useful for identifying correlations and patterns.
Transforming Data Analysis with Descriptive Statistics
1. Improved Decision Making
Descriptive statistics provide a clear and concise summary of data, helping businesses make informed decisions. By understanding the central tendency and variability, businesses can identify trends, detect anomalies, and make data-driven decisions.
2. Enhanced Data Visualization
Graphical representations such as histograms, box plots, and scatter plots make data more accessible and understandable. Visualizing data allows businesses to quickly grasp complex information, facilitating better communication and interpretation.
3. Identifying Patterns and Trends
Descriptive statistics help in identifying patterns and trends within data sets. By analyzing measures of central tendency and variability, businesses can uncover underlying patterns that may not be immediately apparent, leading to valuable insights.
4. Benchmarking and Performance Measurement
Descriptive statistics enable businesses to benchmark their performance against industry standards or historical data. By comparing mean, median, and standard deviation, businesses can assess their performance and identify areas for improvement.
5. Risk Management
Understanding data variability through measures like standard deviation helps businesses assess risk. High variability may indicate potential risks or instability, allowing businesses to take proactive measures to mitigate these risks.
Practical Applications of Descriptive Statistics in Business
1. Marketing Analysis
In marketing, descriptive statistics help in analyzing customer data, such as purchase behavior, preferences, and demographics. By understanding the central tendencies and variability, businesses can tailor their marketing strategies to target specific customer segments effectively.
2. Financial Analysis
Descriptive statistics are crucial in financial analysis for summarizing revenue, expenses, and profitability. By analyzing historical financial data, businesses can identify trends, forecast future performance, and make strategic financial decisions.
3. Quality Control
In manufacturing, descriptive statistics are used to monitor and improve product quality. By analyzing production data, businesses can identify defects, measure process variability, and implement quality control measures to enhance product quality.
4. Human Resources
Descriptive statistics aid in analyzing employee performance, satisfaction, and retention rates. By summarizing HR data, businesses can identify trends, address workforce issues, and develop strategies to improve employee satisfaction and productivity.
Conclusion
Descriptive statistics play a vital role in transforming data analysis, providing businesses with valuable insights and driving strategic decisions. By summarizing and visualizing data, businesses can make informed decisions, identify patterns, manage risks, and enhance performance. Embracing descriptive statistics as part of your data analysis toolkit can unlock significant business insights and pave the way for success in a data-driven world.



